このページではより実践的な手法として、launchファイルからlaunchファイルへパラメータを渡して実行するlaunchのネスト(入れ子)構造を紹介していきます。
少し難易度が上がるかもしれませんが、なるべく理解しやすいようシンプルに説明していきますね!
以降で紹介するサンプルコードは全てROSパッケージ化した状態でGitHubに載せています。
自分の環境で実行して挙動を確認してみたい場合は下記からクローンして使用してください。
本ページで使用するコード
launchファイルへパラメータを渡して実行する
ここまでLaunchファイルからlaunch_ros.actions.Nodeの引数を通して各ノードに起動条件を設定した上でノードを起動することができることを説明してきました。
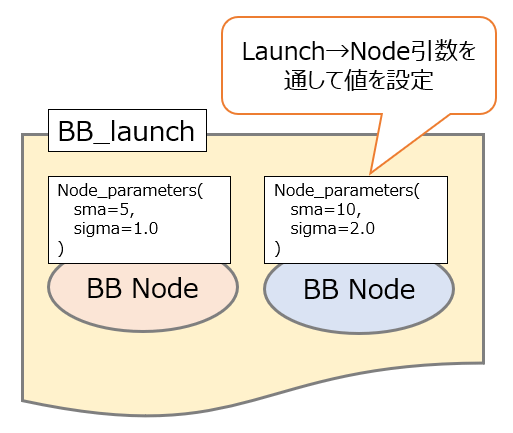
実はこのlaunchファイル、自分自身にも引数を設定することができて、外部からlaunchファイルへ値を渡すことができるようになります。
また、launchファイルからlaunchファイルを呼び出すこともできるため、引数を伴ったlaunchファイルのネスト(入れ子)構造を構築することができます。
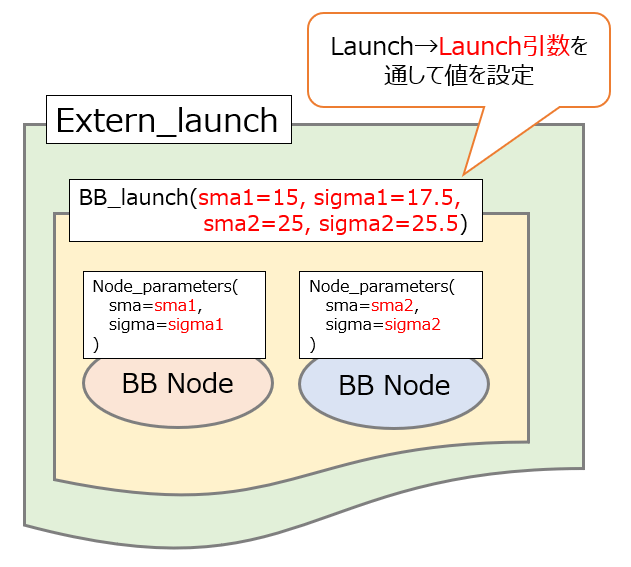
システムの規模が大きくなってくると、複数のlaunchファイルに分割した方が起動構成の見通しが良くなって管理しやすくなるメリットがあるので、是非こちらの使い方も覚えておきましょう!
引数を伴ったlaunchファイルの記述方法
では、引数の値を渡せるようにするためのlaunchファイルの記述内容を見ていきましょう!
ファイル名bb_param_value_ext_launch.pyを作成し、下記のように記述します。
(bb_param_value_launch.pyから変更した行をハイライトしています。)
from launch.launch_description import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument
from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration
from launch_ros.actions import Node
def generate_launch_description() -> LaunchDescription:
# Launch引数名の定義
VN_NS1_SMA = "ns1_sma"
VN_NS1_SIGMA = "ns1_sigma"
VN_NS2_SMA = "ns2_sma"
VN_NS2_SIGMA = "ns2_sigma"
# Launch引数の値を受け取るための変数定義
lc_ns1sma = LaunchConfiguration(VN_NS1_SMA)
lc_ns1sigma = LaunchConfiguration(VN_NS1_SIGMA)
lc_ns2sma = LaunchConfiguration(VN_NS2_SMA)
lc_ns2sigma = LaunchConfiguration(VN_NS2_SIGMA)
# Launch引数の宣言
# ※"default_value"を設定した場合、外部から呼び出されたときに引数が指定されていないと
# "default_value"の値が初期値として設定される
# ※"default_value"を設定しない場合、外部から呼び出されたときに引数が指定されていないと
# エラーとなり、処理を停止する。
declare_ns1sma_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
VN_NS1_SMA,
default_value="33",
description="Bollinger-Bands SMA in namespace1",
)
declare_ns1sigma_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
VN_NS1_SIGMA,
default_value="3.3",
description="Bollinger-Bands Sigma in namespace1",
)
declare_ns2sma_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
VN_NS2_SMA,
# default_value="55",
description="Bollinger-Bands SMA in namespace2",
)
declare_ns2sigma_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
VN_NS2_SIGMA,
# default_value="5.5",
description="Bollinger-Bands Sigma in namespace2",
)
# ノード・アクションの定義
node_act1 = Node(
package="ros2_example",
executable="bb_param",
name=None,
namespace="name_space_1",
parameters=[{"sma": lc_ns1sma, "sigma": lc_ns1sigma}],
output="screen",
)
node_act2 = Node(
package="ros2_example",
executable="bb_param",
name=None,
namespace="name_space_2",
parameters=[{"sma": lc_ns2sma, "sigma": lc_ns2sigma}],
output="screen",
)
# LaunchDescriptionオブジェクトの生成
ld = LaunchDescription()
# Launch引数アクションの追加
ld.add_action(declare_ns1sma_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_ns1sigma_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_ns2sma_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_ns2sigma_cmd)
# ノード・アクションの追加
ld.add_action(node_act1)
ld.add_action(node_act2)
return ldまずは引数名の定義になります。
8~12行目が引数名の定義になります。
今回の例ではlaunch引数を4つ定義するので、引数名も4つ定義します。
# Launch引数名の定義
VN_NS1_SMA = "ns1_sma"
VN_NS1_SIGMA = "ns1_sigma"
VN_NS2_SMA = "ns2_sma"
VN_NS2_SIGMA = "ns2_sigma"次は定義した4つの引数名に渡された値を受け取るための変数を定義します。
変数定義はlaunch.substitutions.LaunchConfiguration()を使用します。
第1引数には先ほど定義した引数名を指定します。
そうすることでlaunch.substitutions.LaunchConfiguration()で定義した変数と引数名が紐づくようになります。
# Launch引数の値を受け取るための変数定義
lc_ns1sma = LaunchConfiguration(VN_NS1_SMA)
lc_ns1sigma = LaunchConfiguration(VN_NS1_SIGMA)
lc_ns2sma = LaunchConfiguration(VN_NS2_SMA)
lc_ns2sigma = LaunchConfiguration(VN_NS2_SIGMA)定義した変数はlaunch_ros.actions.Nodeのparameters引数に設定します。(52、60行目)
# ノード・アクションの定義
node_act1 = Node(
package="ros2_example",
executable="bb_param",
name=None,
namespace="name_space_1",
parameters=[{"sma": lc_ns1sma, "sigma": lc_ns1sigma}],
output="screen",
)
node_act2 = Node(
package="ros2_example",
executable="bb_param",
name=None,
namespace="name_space_2",
parameters=[{"sma": lc_ns2sma, "sigma": lc_ns2sigma}],
output="screen",
)最後に、定義した4つの引数名をlaunchファイル引数として外部から渡せるように引数宣言をします。
引数宣言にはlaunch.actions.DeclareLaunchArgument()を使用します。
# Launch引数の宣言
# ※"default_value"を設定した場合、外部から呼び出されたときに引数が指定されていないと
# "default_value"の値が初期値として設定される
# ※"default_value"を設定しない場合、外部から呼び出されたときに引数が指定されていないと
# エラーとなり、処理を停止する。
declare_ns1sma_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
VN_NS1_SMA,
default_value="33",
description="Bollinger-Bands SMA in namespace1",
)
declare_ns1sigma_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
VN_NS1_SIGMA,
default_value="3.3",
description="Bollinger-Bands Sigma in namespace1",
)
declare_ns2sma_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
VN_NS2_SMA,
# default_value="55",
description="Bollinger-Bands SMA in namespace2",
)
declare_ns2sigma_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
VN_NS2_SIGMA,
# default_value="5.5",
description="Bollinger-Bands Sigma in namespace2",
)launch.actions.DeclareLaunchArgument()の引数説明
- 第1引数:
launchファイルの引数名。
外部から引数指定するときはここで指定した名前で値を設定することになる。 - default_value(オプション):
launchファイルの呼び出し側で引数の指定が省略された場合に設定されるデフォルト値。
挙動はPythonやC++関数のデフォルト引数と同じで、本引数の指定を省略した場合はlaunchファイルの呼び出し側での引数の指定が必須になる。
(本引数の指定を省略した上で、launchファイルの呼び出し側で引数の指定が省略された場合はエラーとなる。) - description(オプション):
引数の説明。
オプション引数だが、できるだけ書くようにしよう!

4つの引数名の内、default_valueの指定あり/なしに分けて引数宣言してみました。
あとで挙動の違いを確認してみましょう!
default_value指定あり- VN_NS1_SMA(“ns1_sma”)
- VN_NS1_SIGMA(“ns1_sigma”)
default_value指定なし- VN_NS2_SMA(“ns2_sma”)
- VN_NS2_SIGMA(“ns2_sigma”)
なお、launch.actions.DeclareLaunchArgument()は定義場所を見てもらうとわかる通り、actions(アクション)であるため、LaunchDescriptionオブジェクトに追加する必要があります。
# Launch引数アクションの追加
ld.add_action(declare_ns1sma_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_ns1sigma_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_ns2sma_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_ns2sigma_cmd)さて、これで引数で値渡しが可能なlaunchファイルができました。
コマンドラインから引数を渡してみる
そうしたら、一旦ここで作成したbb_param_value_ext_launch.pyがlaunch引数を受け取れるかどうか単体で動作を確認してみます。
colconビルドとワークスペース情報の更新を行いましょう。
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source install/local_setup.bashまずは引数を与えずにbb_param_value_ext_launch.pyを実行してみます。
$ ros2 launch ros2_example bb_param_value_ext_launch.py
引数を与えないと下記のような結果となります。
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /home/***
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[ERROR] [launch]: Caught exception in launch (see debug for traceback): Included launch description missing required argument 'ns2_sma' (description: 'Bollinger-Bands SMA in namespace2'), given: []「指定が必須な引数 ‘ns2_sma’ に間違いがあります。」と怒られました。
引数ns2_smaは指定必須引数でありながら引数指定を省略したため上記のようなエラーが発生しました。
指定必須引数はns2_smaとns2_sigmaのため、次はこの2つの引数に値を指定して実行してみましょう!
$ ros2 launch ros2_example bb_param_value_ext_launch.py ns2_sma:=10 ns2_sigma:=15.5実行するとname_space_2.bb_paramノードのパラメータに引数で指定した値が設定されて実行されているのがわかると思います。
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /home/***
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [bb_param-1]: process started with pid [3194]
[INFO] [bb_param-2]: process started with pid [3196]
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: bb_param start!
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: bb_param start!
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: sma:[33] sigma:[3.3]
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: sma:[10] sigma:[15.5]
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: sma:[33] sigma:[3.3]
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: sma:[10] sigma:[15.5]
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: sma:[33] sigma:[3.3]
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: sma:[10] sigma:[15.5]

ns1_smaとns1_sigmaの引数指定は省略したため、name_space_1.bb_paramノードはデフォルト値のsma=33とsigma=3.3がそれぞれ設定されて動作しているのがわかりますね!
次はオプション引数のns1_smaとns1_sigmaにもコマンドラインから値を設定して実行してみます。
$ ros2 launch ros2_example bb_param_value_ext_launch.py ns2_sma:=10 ns2_sigma:=15.5 ns1_sma:=99 ns1_sigma:=99.9実行するとname_space_1.bb_paramノードのパラメータ値も引数で指定した値が設定されて実行されるようになります。
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /home/***
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [bb_param-1]: process started with pid [3290]
[INFO] [bb_param-2]: process started with pid [3292]
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: bb_param start!
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: bb_param start!
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: sma:[10] sigma:[15.5]
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: sma:[99] sigma:[99.9]
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: sma:[10] sigma:[15.5]
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: sma:[99] sigma:[99.9]起動しようとしているlaunchファイルに引数があるか否かはオプション-sで確認することができます。
引数が定義されている場合はlaunch.actions.DeclareLaunchArgument()で指定した引数名、default_value(オプション)、description(オプション)がここで表示されます。
$ ros2 launch ros2_example bb_param_value_ext_launch.py -s
Arguments (pass arguments as '<name>:=<value>'):
'ns1_sma':
Bollinger-Bands SMA in namespace1
(default: '33')
'ns1_sigma':
Bollinger-Bands Sigma in namespace1
(default: '3.3')
'ns2_sma':
Bollinger-Bands SMA in namespace2
'ns2_sigma':
Bollinger-Bands Sigma in namespace2
launchファイルから引数を渡してみる
launchファイル単体でlaunch引数が受け取れることが確認できたため、次はlaunchファイルからlaunchファイルに引数を渡してノードが起動できることを確認していきましょう!
bb_param_value_ext_launch.pyファイルを呼び出すlaunchファイルとしてextern_value_launch.pyを作成し、下記の内容を記述します。
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch.launch_description import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
def generate_launch_description() -> LaunchDescription:
# Launch引数名の定義
VN_NS1_SMA = "ns1_sma"
VN_NS1_SIGMA = "ns1_sigma"
VN_NS2_SMA = "ns2_sma"
VN_NS2_SIGMA = "ns2_sigma"
# パッケージとLaunchディレクトリの取得
package_dir = get_package_share_directory("ros2_example")
launch_dir = os.path.join(package_dir, "launch")
# Launchアクションの定義
# ロードするLaunchファイルを指定する
# Launch引数はlaunch_argumentsで指定する
launch_cmd = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(
os.path.join(launch_dir, "bb_param_value_ext_launch.py")
),
launch_arguments={
VN_NS1_SMA: "100",
VN_NS1_SIGMA: "100.11",
VN_NS2_SMA: "300",
VN_NS2_SIGMA: "300.33",
}.items(),
)
# LaunchDescriptionオブジェクトの生成
ld = LaunchDescription()
# Launchアクションの追加
ld.add_action(launch_cmd)
return ldまずはlaunch引数名の定義になります。
値を渡す側と受け取る側の引数名は一致している必要があります。
# Launch引数名の定義
VN_NS1_SMA = "ns1_sma"
VN_NS1_SIGMA = "ns1_sigma"
VN_NS2_SMA = "ns2_sma"
VN_NS2_SIGMA = "ns2_sigma"次はディレクトリ情報の取得です。
15~17行目で呼び出すlaunchファイルの保存先ディレクトリを取得しています。
# パッケージとLaunchディレクトリの取得
package_dir = get_package_share_directory("ros2_example")
launch_dir = os.path.join(package_dir, "launch")そして次が肝となる本launchファイルからbb_param_value_ext_launch.pyファイルに引数を渡して呼び出す記述となります。
# Launchアクションの定義
# ロードするLaunchファイルを指定する
# Launch引数はlaunch_argumentsで指定する
launch_cmd = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(
os.path.join(launch_dir, "bb_param_value_ext_launch.py")
),
launch_arguments={
VN_NS1_SMA: "100",
VN_NS1_SIGMA: "100.11",
VN_NS2_SMA: "300",
VN_NS2_SIGMA: "300.33",
}.items(),
)launchファイルを呼び出すにはlaunch.actions.IncludeLaunchDescription()を使います。
第1引数にはbb_param_value_ext_launch.pyファイル格納先をフルパスを指定し、オプション引数launch_argumentsにlaunch引数を指定します。
launch.actions.IncludeLaunchDescription()もactions(アクション)のため、LaunchDescriptionオブジェクトに追加する必要があります。
# Launchアクションの追加
ld.add_action(launch_cmd)では、実行して動作を確認していきます。
$ ros2 launch ros2_example extern_value_launch.py以下、実行結果です。
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /home/***
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [bb_param-1]: process started with pid [4680]
[INFO] [bb_param-2]: process started with pid [4682]
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: bb_param start!
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: bb_param start!
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: sma:[100] sigma:[100.11]
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: sma:[300] sigma:[300.33]
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: sma:[100] sigma:[100.11]
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: sma:[300] sigma:[300.33]
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: sma:[100] sigma:[100.11]パラメータ値にextern_value_launch.pyで指定した値がちゃんと設定されていることが確認できました!
launchファイルからYAMLを渡してみる
extern_value_launch.pyではlaunch引数に値を直接指定して渡していましたが、YAMLファイルを渡すこともできます。
bb_param_yaml_ext_launch.pyファイルを呼び出すlaunchファイルextern_yaml_launch.pyを作成して動作を確認してみます。
(基本的に値の指定をYAMLファイル指定に置き換えているだけですので説明は省きます。)
<YAMLファイル(bb_param_ext.yaml)>
/name_space_1/bb_param:
ros__parameters:
sma: 9
sigma: 1.9
/name_space_2/bb_param:
ros__parameters:
sma: 90
sigma: 2.9<呼び出される側のLaunch(bb_param_yaml_ext_launch.py)ファイル>
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch.launch_description import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument
from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration
from launch_ros.actions import Node
def generate_launch_description() -> LaunchDescription:
# 読み込ませるYAMLファイル名の定義
BB_PARAM_YAML = "bb_param.yaml"
# Launch引数名の定義
VN_BB_PARAM = "bb_param"
# パッケージ・ディレクトリの取得
package_dir = get_package_share_directory("ros2_example")
# Launch引数の値を受け取るための変数定義
lc_bb_param_yaml = LaunchConfiguration(VN_BB_PARAM)
# Launch引数の宣言
# ※"default_value"を設定した場合、外部から呼び出されたときに引数が指定されていないと
# "default_value"の値が初期値として設定される
# ※"default_value"を設定しない場合、外部から呼び出されたときに引数が指定されていないと
# エラーとなり、処理を停止する。
declare_bb_params_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
VN_BB_PARAM,
default_value=os.path.join(package_dir, "params", BB_PARAM_YAML),
description="Full path to the ROS2 parameters file to use for the launched node",
)
# ノード・アクションの定義
node_act1 = Node(
package="ros2_example",
executable="bb_param",
name=None,
namespace="name_space_1",
parameters=[lc_bb_param_yaml],
output="screen",
)
node_act2 = Node(
package="ros2_example",
executable="bb_param",
name=None,
namespace="name_space_2",
parameters=[lc_bb_param_yaml],
output="screen",
)
# LaunchDescriptionオブジェクトの生成
ld = LaunchDescription()
# Launch引数アクションの追加
ld.add_action(declare_bb_params_cmd)
# ノード・アクションの追加
ld.add_action(node_act1)
ld.add_action(node_act2)
return ld
<呼び出す側のLaunch(extern_yaml_launch.py)ファイル>
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch.launch_description import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
def generate_launch_description() -> LaunchDescription:
# 読み込ませるYAMLファイル名の定義
BB_PARAM_YAML = "bb_param_ext.yaml"
# Launch引数名の定義
VN_BB_PARAM = "bb_param"
# パッケージとLaunchディレクトリの取得
package_dir = get_package_share_directory("ros2_example")
launch_dir = os.path.join(package_dir, "launch")
# YAMLファイル格納場所のフルパスを取得
yaml_fullpath = os.path.join(package_dir, "params", BB_PARAM_YAML)
# Launchアクションの定義
# ロードするLaunchファイルを指定する
# Launch引数はlaunch_argumentsで指定する
launch_cmd = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(
os.path.join(launch_dir, "bb_param_yaml_ext_launch.py")
),
launch_arguments={
VN_BB_PARAM: yaml_fullpath,
}.items(),
)
# LaunchDescriptionオブジェクトの生成
ld = LaunchDescription()
# Launchアクションの追加
ld.add_action(launch_cmd)
return ldlaunch引数をYAMLファイルにした場合の引数確認オプション-s結果は下記のようになります。
$ ros2 launch ros2_example extern_yaml_launch.py -s
Arguments (pass arguments as '<name>:=<value>'):
'bb_param':
Full path to the ROS2 parameters file to use for the launched node
(default: '/home/***/ros2_example/params/bb_param.yaml')そして、実行結果は下記のようになります。
$ ros2 launch ros2_example extern_yaml_launch.py
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /home/***
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [bb_param-1]: process started with pid [4772]
[INFO] [bb_param-2]: process started with pid [4774]
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: bb_param start!
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: bb_param start!
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: sma:[90] sigma:[2.9]
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: sma:[9] sigma:[1.9]
[bb_param-2] [INFO][name_space_2.bb_param]: sma:[90] sigma:[2.9]
[bb_param-1] [INFO][name_space_1.bb_param]: sma:[9] sigma:[1.9]





コメント